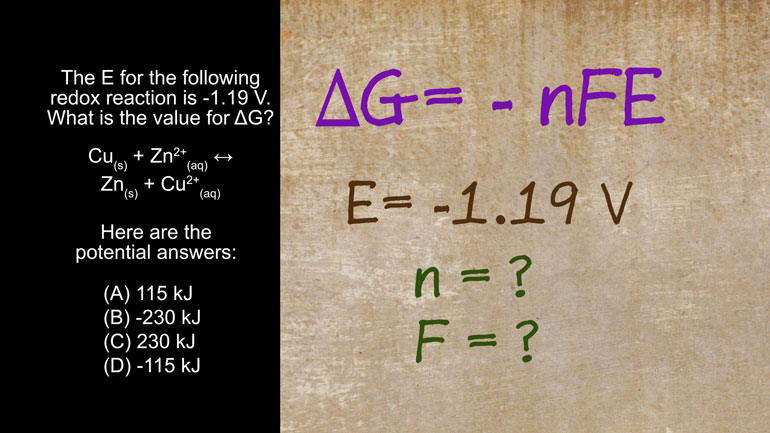ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
AP Chemistry 2.3 Chemical Reaction Rates 3 Views
Share It!
Description:
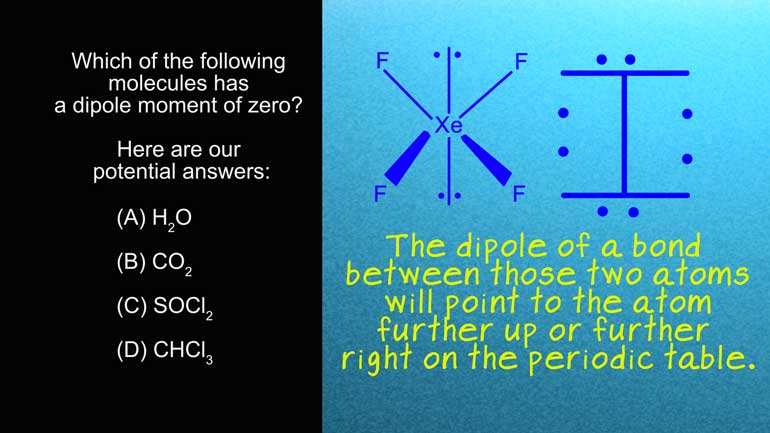
AP Chemistry 2.3 Chemical Reaction Rates. What is the experimental rate law for this reaction?
Transcript
- 00:03
And here’s your Shmoop du jour, brought to you by reaction rate.
- 00:07
Hey, think fast! …Ooh, that’s gotta hurt. [Boy strikes a ball with a bat and ball hits man in face]
- 00:10
Sorry…
- 00:11
Here’s today’s problem:
- 00:12
The reaction: A + B yields C was run three different times, and each time, the concentrations
Full Transcript
- 00:18
of the reactants were altered.
- 00:20
The reaction rate was also measured each time the reaction was run, as shown in the table.
- 00:25
What is the experimental rate law for this reaction? [Table of experiment measurements]
- 00:28
And here are your potential answers.
- 00:31
To answer this question, we’ll need to examine the experimental data and deduce the appropriate
- 00:38
rate law for this reaction. [Doctor with a zombie-looking man on a table]
- 00:41
The reactants here are species A and B. In the three experiments shown in the table,
- 00:46
the initial concentrations of A and B are varied.
- 00:49
Because everyone is special in their own way. [Woman hugging a young boy]
- 00:51
Anyway, between experiments 1 and 3, the initial concentration of A is doubled while the initial
- 00:58
concentration of B stays the same.
- 01:00
We can use these two data points to find out how the rate depends on the concentration [Rate swinging and A grabs it]
- 01:04
of species A without worrying about species B.
- 01:06
So, what is the dependence on A? [A and B sitting on a couch]
- 01:09
When the initial concentration of A is doubled, the rate stays the same, so it doesn’t depend
- 01:14
on A at all.
- 01:15
Kind of like how your parents don’t depend on you to do the dishes anymore. [Girl sitting on a couch with a pizza]
- 01:18
Yeah, we know, you'd get to them "in a minute".
- 01:20
Whatever you say.
- 01:21
So between experiments 1 and 2, the initial concentration of B is doubled, while the initial
- 01:26
concentration of A stays the same.
- 01:28
With these two points, we can find how the rate depends on species B.
- 01:31
When the concentration of B is doubled, the rate increases by four times. [B increases in size and a hand holding 4 fingers appears]
- 01:36
That means the rate depends on B squared.
- 01:38
That's not quite like us… when our concentration is doubled, we make it through class without
- 01:42
falling asleep.
- 01:43
We know.
- 01:44
Not all heroes wear capes. [People staying awake in a classroom]
- 01:45
Anyway, now we know that the rate depends on the concentration of B squared, but it
- 01:50
doesn’t depend on A at all.
- 01:51
Looking at our answers, choice (A) fits the bill, as all the others include some dependence
- 01:56
on species A. So choice (A) is the right answer.
- 01:59
Now it’s time to get those dishes done. [A collection of dirty dishes]
- 02:03
Hey, where are you going?
- 02:05
Oh, brother.
- 02:06
Seriously, maybe your brother will do them instead. [Brother and sister run away]
Up Next
AP Chemistry 1.3 Chemical Reaction Rates. What is the overall order of the reaction?
Related Videos
AP Chemistry 1.4 Chemical Reaction Rates. What are the correct units for a second order rate constant?
AP Chemistry 1.5 Chemical Reaction Rates. What is the rate law for the reaction?
AP Chemistry 3.2 Laws of Thermodynamics. What is the value for ΔG?