Viral Genomes
The genomes of viruses are just like every other genome: they contain all the genes necessary to replicate themselves. However, viruses are very lazy, and they use most of the host cell's machinery to make what they need to replicate. Kind of like that time we let that carnie into our house, then when we came back the dryer was gone…and there were twelve carnies and a ring toss game in its place. Yeah, just like that.
Viruses have genes that encode a minimum of two proteins:
Types of Virus Genomes
Wow. That was a lot, right? Well, it gets worse. While most genomes are non-segmented (the genome is all on one piece of RNA or DNA), some genomes are segmented, meaning there are several fragments of genetic material that make a complete virus genome. Also, some genomes are linear, meaning that there is a beginning and end to the genome, while other genomes are circular (no beginning and no end. Kind of like that friendship song, except by "friends" we mean "piles of microscopic goo").
That seems like a lot of information overload, and we sympathize. For something so small and seemingly simple (like "I can't believe it's not butter"), viruses are very complex (like the ingredients of "I can't believe it's not butter"). The important thing is that if you can tell the difference between RNA and DNA virus, and if it is linear or circular, and if it is segmented or non-segmented, you can immediately tell a lot about a virus. So, we attached a table to serve as a cheat sheet for virus genomes.
Viruses have genes that encode a minimum of two proteins:
- Replicase – an enzyme that replicates the genome
- Capsid – a protein that protects the genome.
- Protease – enzyme that processes viral proteins and allows assembly or maturation to infect other virus cells.
- Glycoprotein – (enveloped viruses only) allows virus to enter a cell, targets specific cell types for virus, and aids in virus assembly.
- Host shutoff proteins – virus proteins that shut off host activities so only virus genes get made.
- Anti-host defense proteins – the number and type of these different genes will vary, depending on the virus. These proteins prevent the host defense mechanism from stopping virus replication.

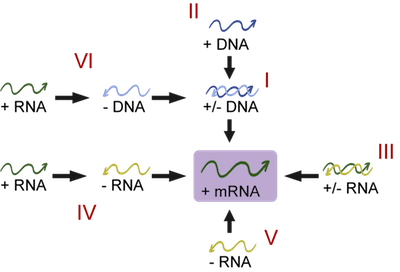
Types of Virus Genomes
Wow. That was a lot, right? Well, it gets worse. While most genomes are non-segmented (the genome is all on one piece of RNA or DNA), some genomes are segmented, meaning there are several fragments of genetic material that make a complete virus genome. Also, some genomes are linear, meaning that there is a beginning and end to the genome, while other genomes are circular (no beginning and no end. Kind of like that friendship song, except by "friends" we mean "piles of microscopic goo").
That seems like a lot of information overload, and we sympathize. For something so small and seemingly simple (like "I can't believe it's not butter"), viruses are very complex (like the ingredients of "I can't believe it's not butter"). The important thing is that if you can tell the difference between RNA and DNA virus, and if it is linear or circular, and if it is segmented or non-segmented, you can immediately tell a lot about a virus. So, we attached a table to serve as a cheat sheet for virus genomes.
| Virus Type | Genome ds (double stranded) ss (single Stranded) | Example | What It Tells Us |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | dsDNA | Adenoviruses, Herpesviruses, and Poxviruses | Virus can use host machinery to make mRNA, and replicate virus |
| II | ssDNA (+) | Parvoviruses | Need DNA polymerase to make negative strand, can use host machinery to make mRNA |
| III | dsRNA | Reoviruses | Needs RNA polymerase to replicate itself as well as make mRNA. |
| IV | ssRNA (+) | Poliovirus and Ebola Virus | Needs RNA polymerase to replicate itself. Genome also serves as mRNA. |
| V | ssRNA (-) | Influenza virus, Hantavirus | Needs RNA polymerase to replicate itself as well as make mRNA |
| - | ssRNA (+) | Retroviruses, HIV | Makes cDNA that integrates into host genome, which makes mRNA and proteins |
| - | Segmented | Influenza | When making viruses, can mix and match segments to allow virus to more easily evolve |
| - | Non-segmented | HIV, Poxvirus | Evolution is more difficult. Requires more error-prone polymerase |
| - | Linear | Needs a primer to start replication from one end of genome. | |
| - | Circular | Poxvirus, Herpesvirus | Replication starts anywhere on the genome (but often has a specific origin of replication) |