ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
Evolution Videos 10 videos
AP Biology 2.3 Evolution. What did the Urey-Miller experiments do?
AP Biology 4.1 Evolution. When or where is allopatric speciation likely seen?
AP Biology 3.2 Evolution 2 Views
Share It!
Description:
AP Biology 3.2 Evolution. What is the comparison of species that live in different habitats across the globe called?
Transcript
- 00:04
Here’s your Shmoop du jour, brought to you by habitats.
- 00:07
Which technically does include a teenager's bedroom, though we're not sure how anything [Teenage boy in his bedroom]
- 00:11
manages to live in there....
- 00:13
Check out the following statement…
- 00:15
The comparison of species that live in different habitats across the globe is called this.
Full Transcript
- 00:20
And here are the potential answers.
- 00:26
All right, let's start by eliminating answer “A”.
- 00:30
Homology is the existence of shared ancestry between a pair of structures in different [A monkey and a man sitting together]
- 00:35
species.
- 00:36
Such a trait would be most evident if you were to purchase a necktie for your fave giraffe. [Person giving a gift to a giraffe]
- 00:41
Since giraffes have the same number of neck bones as humans do, you could theoretically
- 00:46
get away with buying your giraffe-pal a tie from your local Macy's. [A giraffe wearing a tie]
- 00:50
While that'd be a nice gesture, it wouldn't prove anything about why the giraffe lives
- 00:54
where he lives, so answer “A” is incorrect.
- 00:57
How about answer “C”?
- 00:58
Vestigial organs inhabit the body, but have no functional value to the person. [Human body with vestigial organs]
- 01:04
The appendix comes to mind.
- 01:05
Though to be fair, there's always a chance the appendix will turn into a ticking time [Surgeons removing a persons appendix]
- 01:10
bomb, so at least it has the element of surprise working in its favor.
- 01:13
However, the appendix and other vestigial organs aren't the answer we're looking for.
- 01:17
Moving on.
- 01:18
How about “D”?
- 01:20
Comparative embryology DOES compare species, but only to gather evidence of evolution.
- 01:25
It's a worthwhile field.
- 01:26
It helped us find out the bird evolved from the dinosaur, and that's just...ridiculous. [Diagram of a dinosaur and bird structures]
- 01:31
Hah.
- 01:32
Look at that little dinky bird. [Little bird hopping in the park]
- 01:34
Anyway.
- 01:36
Answer “D” isn't our winner.
- 01:37
That leaves “B”.
- 01:38
And guess what?
- 01:39
The comparison of species that live in different habitats across the globe just happens to
- 01:43
be called biogeography.
- 01:45
Inquiring scientists want to know why marsupials are only found in Australia. [A scientist in the lab and a marsupial bounces past]
- 01:50
How did all the flora and fauna wind up where it wound up?
- 01:55
And why isn't there a duo named Flora and Fauna? [Marsupial and flowers on stage]
- 01:58
We'd buy that album.
- 02:01
B is our correct answer.
- 02:02
If you'll excuse us, we have to work on our next screenplay: Jurassic Park 3: Fuzzy Duck [Advert for Jurassic Park 9]
- 02:08
Snuggles.
- 02:09
Aw.
- 02:10
How cute. [A group of girls cuddle a duck]
Related Videos
AP Biology: Biological System Interactions Drill 1, Problem 1. Complete the sentence about a saturated fatty acid.
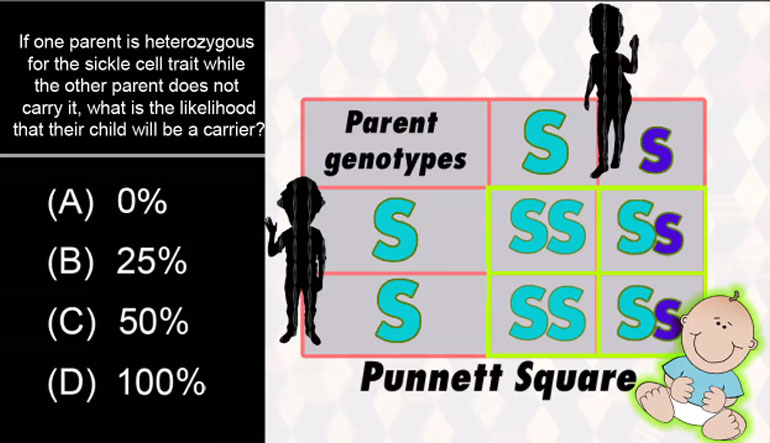
AP Biology: Essential Life Process Information Drill 1, Problem 1. If one parent is heterozygous for the sickle cell trait while the other par...
AP Biology: Evolution Drives the Diversity and Unity of Life Drill 1, Problem 1. The first cells on planet Earth were likely what?
AP Biology: Free Energy and Molecular Building Blocks Drill 1, Problem 1. Which statement incorrectly describes the properties of water?
AP® Biology: Evolution Drives the Diversity and Unity of Life Drill 1, Problem 2. What was likely the first genetic material?