ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
Changes and Conservation Laws Videos 9 videos
AP Physics 2: 1.1 Changes and Conservation Laws. Which of the following statements are true?
AP Physics 2: 2.4 Changes and Conservation Laws. What is the current I1 in the gravy grenade circuit?
AP Physics 2: 1.5 Changes and Conservation Laws. Which of the following statements is correct?
AP Physics 2: 2.5 Changes and Conservation Laws 3 Views
Share It!
Description:
AP Physics 2: 2.5 Changes and Conservation Laws. Which of the following will occur?
Transcript
- 00:03
And here's your shmoop du jour brought to you by charging, charging as
- 00:07
in electricity not as in maxing out credit card at the comic book store [Girl carrying a stack of comic books]
- 00:11
although that is a fun way to spend an afternoon all right a student places two
- 00:15
metal spheres next to each other so that they are tangent at one point the [Student carrying two metal spheres]
- 00:19
student then charges a balloon with negative charge and places it near one
Full Transcript
- 00:22
of the spheres which of the following will occur select two answers and here
- 00:26
are the choices...... all right conduction and induction are different we already know
- 00:35
that since there are different words and all but well we just wanted to say it
- 00:38
out loud the biggest difference is that charge by conduction requires physical [Zombie chasing group of student]
- 00:43
contact in conduction if a negatively charged object touches a neutral object
- 00:48
electrons move from the negative object in parting a negative charge to the [electrons moving to a neutral object]
- 00:52
neutral object but also weakening the negative charge on the first one in
- 00:56
induction there's no physical contact so the negatively charged object doesn't
- 01:01
lose any electrons or any charge instead the negative charge repels negative
- 01:06
particles in the neutrally charged object polarizing it since the [polarised charged particle]
- 01:11
negatively charged balloon doesn't touch the spheres we know we're not dealing [negatively charged balloon near the two spheres]
- 01:15
with conduction answer A) is wrong and answer B) is right this is charged by
- 01:20
induction and as we just discussed charge by induction means the particles [Charges rearranging in a metal sphere]
- 01:25
rearrange themselves so answer C) is also correct because the particles just
- 01:29
rearrange themselves in the neutral spheres answer D) is incorrect there's no
- 01:34
change in the overall charge of the system the particles have moved around
- 01:38
but nothing has been added or taken away from the sphere so the net charge is the [Two spheres stood together]
- 01:43
same well charging by induction is almost like magic you just wave a [magician on stage with negative and positive charged box]
- 01:48
charged object near a neutral one and press those articles go nuts rearranging
- 01:52
themselves maybe for our next trick we can make that credit card bill [girl makes credit card bill disappear]
- 01:56
disappear before your mom finds it.
Related Videos
AP Physics 1: 2.5 Changes and Conservation Law. At what point(s) in this situation is energy lost in any form?
AP Physics 1: 1.4 Waves. Which of the following is technically true for Max as he stands at the edge of oblivion?
AP Physics 1: 1.4 Changes and Conservation Laws. Find the current across R2.
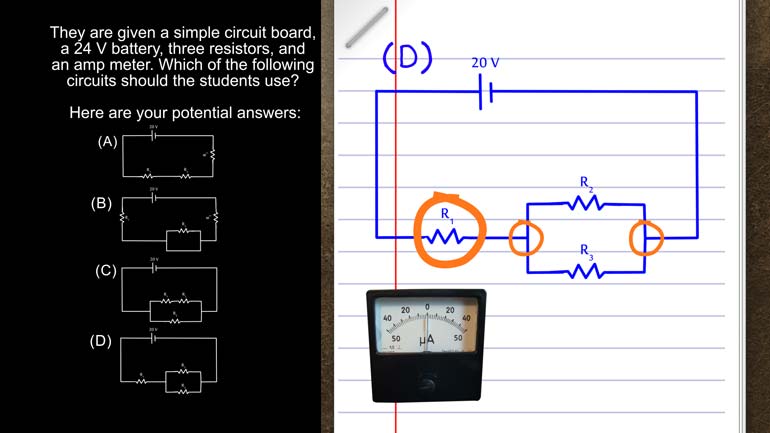
AP Physics 1: 2.4 Changes and Conservation Laws. Which of the following circuits should the students use?
AP Physics 1: 1.5 Waves. What can possibly occur when the two waves reach each other?