ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
AP Videos 1345 videos
AP Biology: Biological System Interactions Drill 1, Problem 1. Complete the sentence about a saturated fatty acid.
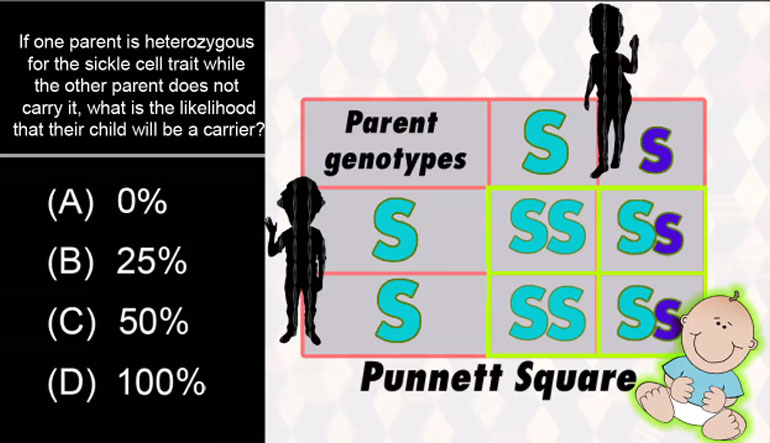
AP Biology: Essential Life Process Information Drill 1, Problem 1. If one parent is heterozygous for the sickle cell trait while the other par...
AP Biology: Evolution Drives the Diversity and Unity of Life Drill 1, Problem 1. The first cells on planet Earth were likely what?
AP Biology 2.5 Essential Life Process Information 7 Views
Share It!
Description:
AP Biology 2.5 Essential Life Process Information. What is the anticodon for the mRNA codon 5'AUG3'?
Transcript
- 00:04
And here’s your Shmoop du jour, brought to you by message machines. [Phone machine flashing]
- 00:07
Ever notice how they always seemed to cut off right before the important part of the–––
- 00:11
Okay, here’s our question:
- 00:15
The anticodon for the mRNA codon 5’AUG3’ is….
- 00:24
And here are our potential answers… First, let’s look at what kind of nucleic [Man holding a magnifying glass]
Full Transcript
- 00:29
acid we’re talking about here… mRNA, otherwise known as messenger RNA.
- 00:35
So we know this is a DNA message that’s being sent out into the cell.
- 00:39
We also know that mRNA should try texting now and then…seriously, who leaves messages [mRNA texting as people laugh]
- 00:44
anymore…? Alright, well RNA is different from DNA in
- 00:47
a variety of ways – it’s single stranded, uses a different sugar in its backbone, and [DNA and RNA stood together]
- 00:54
it uses a different nitrogenous base. They also start with different letters…
- 00:59
Bet you didn’t have that difference on your list. That’s why they pay us the big bucks.
- 01:03
Instead of thymine, RNA uses a base called uracil.
- 01:07
So we can automatically eliminate A and C, as there’s no U for uracil to be seen. [Answers A and C crossed out]
- 01:12
That leaves us with two choices: to B, or not to B…or…to D…or…not…
- 01:16
You get the idea. Let’s take a look at the word anticodon. [Hammer slices word anticodon]
- 01:21
We see “anti” and “code”. What does that mean?
- 01:25
Basically, an anticodon is the opposite of what is being coded. So we need to find the
- 01:29
bases complementary to the ones being encoded by the mRNA. [tRNA molecules added to an mRNA strand]
- 01:32
Remember the base-pairing rules from DNA? A pairs with T and G pairs with C?
- 01:39
Now we’re in mRNA world, so A pairs with U and G…well, G isn't a fan of change. G
- 01:45
still pairs with C. More letters? And we were still wrapping our [Letters floating around mans head]
- 01:49
heads around the whole “R” and “D” difference…
- 01:51
So let’s just write down the opposite of what was coded, “AUG.” A goes with U,
- 01:57
U goes with A, and G goes with C. So the anticodon is UAC. You see?
- 02:04
Now for take two on that message…and we hope we get to finish, because this is important,
- 02:09
make sure you don’t open the–––– [man runs to telephone to answer the message]
Related Videos
AP Biology: Biological System Interactions Drill 1, Problem 1. Complete the sentence about a saturated fatty acid.
AP Biology: Essential Life Process Information Drill 1, Problem 1. If one parent is heterozygous for the sickle cell trait while the other par...
AP Biology: Evolution Drives the Diversity and Unity of Life Drill 1, Problem 1. The first cells on planet Earth were likely what?
AP Biology: Free Energy and Molecular Building Blocks Drill 1, Problem 1. Which statement incorrectly describes the properties of water?
AP® Biology: Evolution Drives the Diversity and Unity of Life Drill 1, Problem 2. What was likely the first genetic material?