ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
AP Physics 2 Videos 59 videos
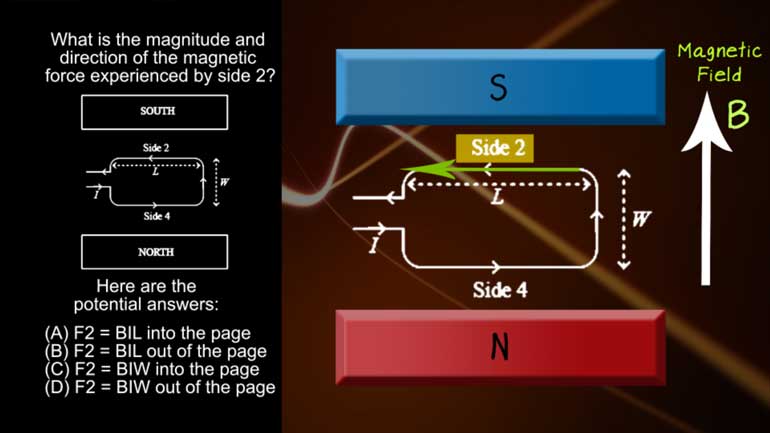
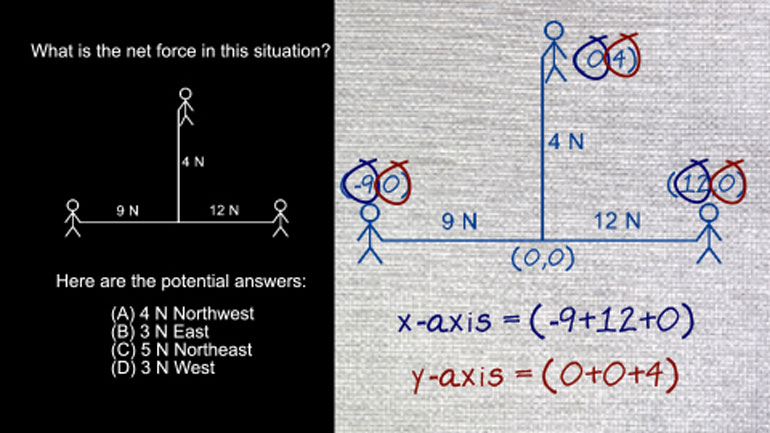
AP Physics 2: 1.1 Properties of Objects and Systems. What is the magnitude and direction of the conventional current in this wire?
AP Physics 2: 1.5 Properties of Objects and Systems. According to the Bohr's model of the atom, which of the following are true?
AP Physics 2: 1.1 Object Interaction and Forces 171 Views
Share It!
Description:
AP Physics 2: 1.1 Object Interaction and Forces. Approximately what fraction of the iron cube is submerged in the liquid mercury?
More Video DetailsTranscript
- 00:00
Thank you We sneak and here's your smoke du jour
- 00:05
brought to you by heavy metal Mercury is a heavy
- 00:08
metal and we were heavy metal to uh we're about
- 00:11
six months aren't following information may be useful Density of
- 00:16
iron is seven point eight eight grand person amir cubed
Full Transcript
- 00:20
dancey of mercury is removed Three agency of water is
- 00:23
one all right Well as the on ly metal that
- 00:26
is liquid at room temperature mercury is a curious metal
- 00:31
If we placed one cubic centimeter iron cube into a
- 00:35
cup of water it would quickly sink However if we
- 00:39
place that same iron cube into a cup of mercury
- 00:42
it would float approximately what fraction of the iron cube
- 00:46
is submerged in the liquid mercury And here the potential
- 00:51
answer All right Well here we go Mercury is a
- 00:56
pretty cool medal It's the only metal that's liquid at
- 00:58
room temperature it's also poisonous mercury is very dance which
- 01:03
means that even heavy things will float in it when
- 01:07
something or someone floats The downward force of gravity is
- 01:11
counterbalanced by the upward force of the material It's A
- 01:15
floating in that upward force is called buoyancy The downward
- 01:20
wait is expressed as density times volume times gravity where
- 01:24
volume equals the total volume of the floating object Well
- 01:28
the buoyant forces expresses the density of the fluid times
- 01:31
the volume of the submerged portion of the floating object
- 01:34
times gravity The buoyant force also equals the weight of
- 01:37
the displaced fluid Well for this question we need to
- 01:40
figure out how much of the little iron block is
- 01:43
submerged in the mercury All right well now we could
- 01:46
probably think a ruler in measure everything and calculated percentage
- 01:48
but well it sounds like a lot of work Luckily
- 01:51
for us there's an easier way in any buoyant system
- 01:53
The fraction of the object that submerged in a fluid
- 01:56
can be figured as a ratio of the densities of
- 01:58
the object and the fur fluid The ratio of the
- 02:01
volume of the submerged portion of the object to its
- 02:04
total volume is equal to the ratio of the density
- 02:07
of the floating object to the density of the fluid
- 02:10
it's floating in it's a good thing we were given
- 02:12
the densities than material when we started this whole thing
- 02:15
Otherwise we'd be a finger deep in mercury and did
- 02:17
we mention the whole poison thing Yeah well the density
- 02:20
of iron is seven point eight eight grams per cubic
- 02:23
centimeter and the density of mercury is thirteen point three
- 02:26
five grams per cubic centimeter When we plugged those numbers
- 02:30
in like this we find that fifty eight percent of
- 02:33
the cube is submerged and we're looking for an approximate
- 02:36
here So answer c is the right choice And as
- 02:40
with a lot of things in physics there's more than
- 02:42
one way to look at buoyancy It just depends on
- 02:44
what we're trying to figure out and sometimes figuring ourselves
- 02:47
out involves leopard print tights and a lot of makeup 00:02:51.015 --> [endTime] Yeah
Related Videos
AP Physics 2: 1.1 Properties of Objects and Systems. What is the magnitude and direction of the conventional current in this wire?
AP Physics 2: 1.5 Properties of Objects and Systems. According to the Bohr's model of the atom, which of the following are true?
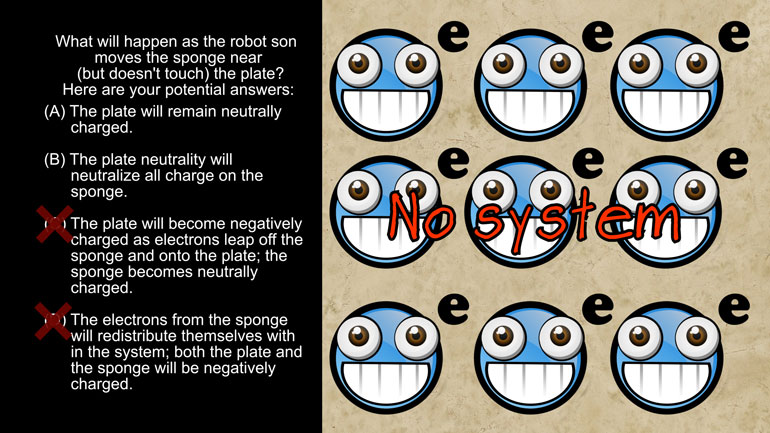
AP Physics 2: 2.2 Properties of Objects and Systems. What will happen as the robot son moves the sponge near (but doesn't touch) the plate?
AP Physics 2: 2.4 Properties of Objects and Systems. How could you show the carnival barker an emission spectrum?