ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
AP Computer Science A Videos 108 videos
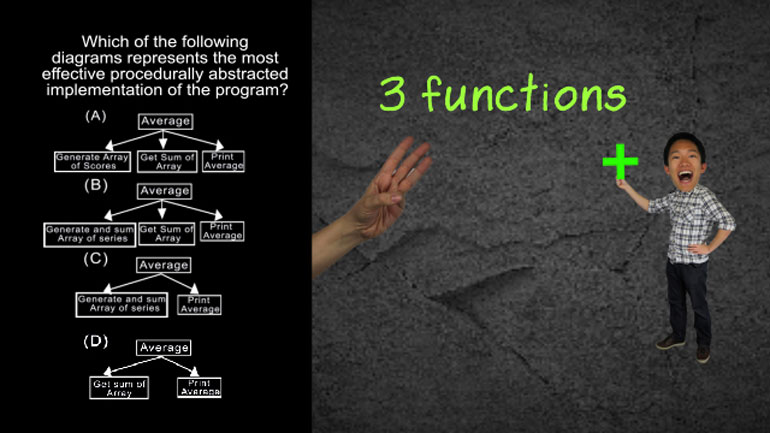
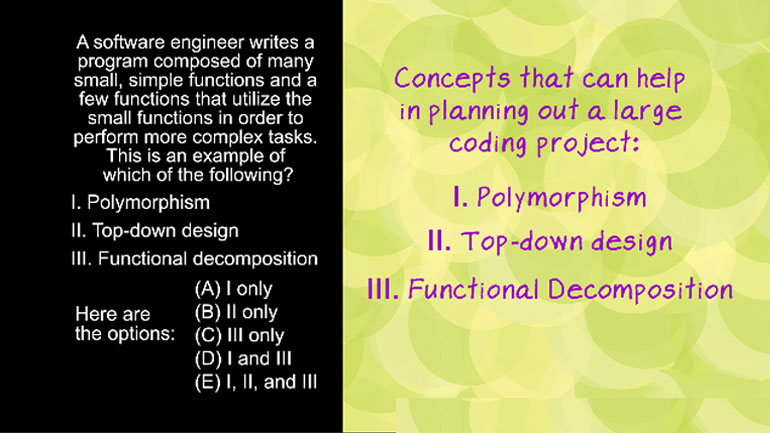
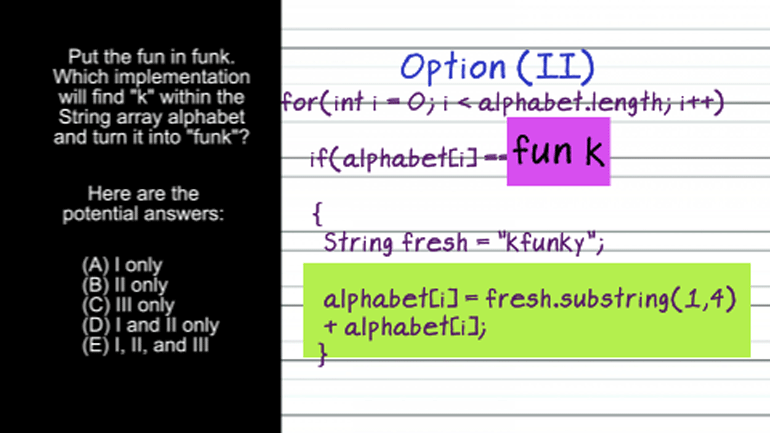
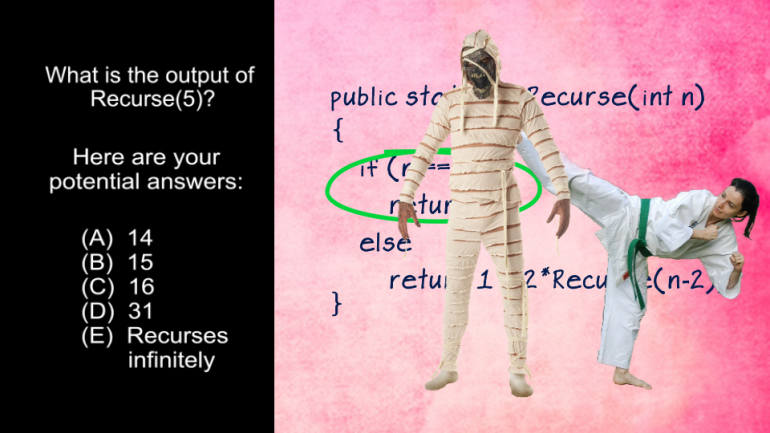
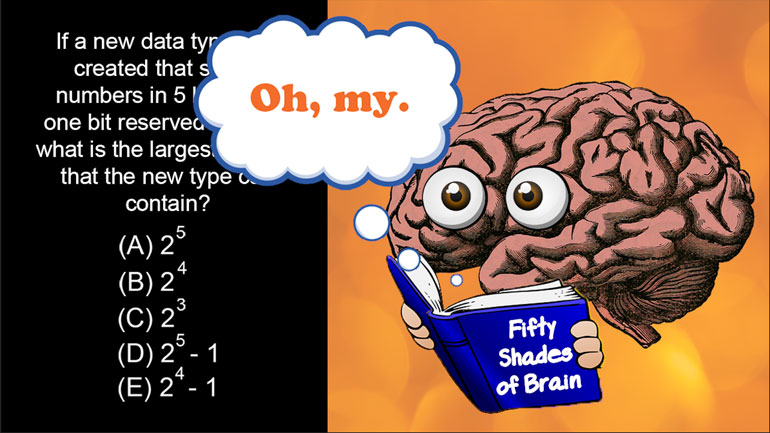
AP Computer Science 1.2 Program Development. Which of the following is correct?
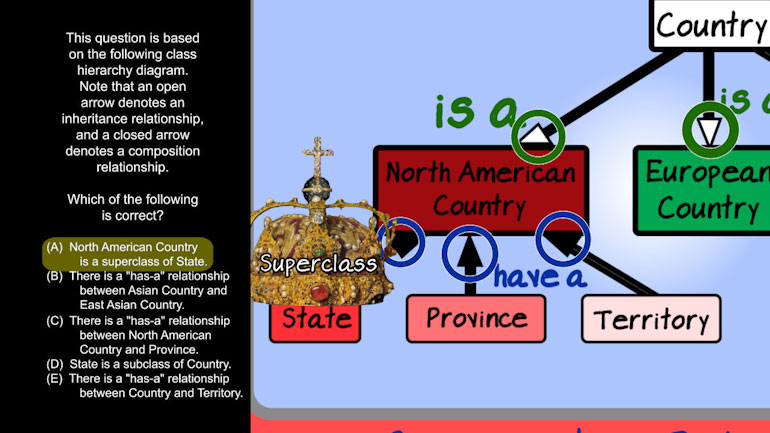
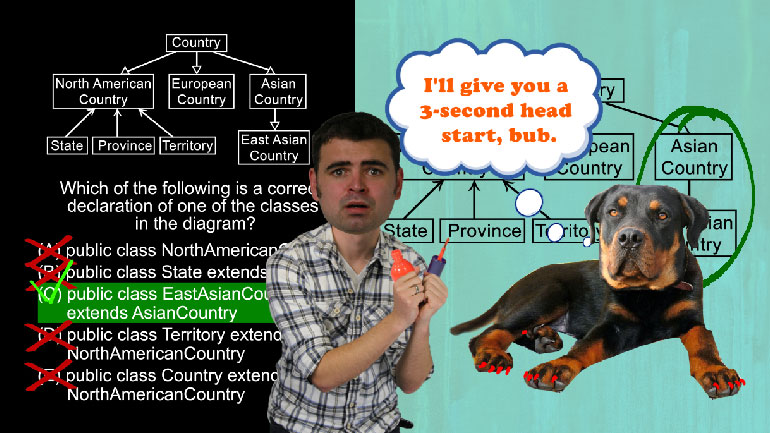
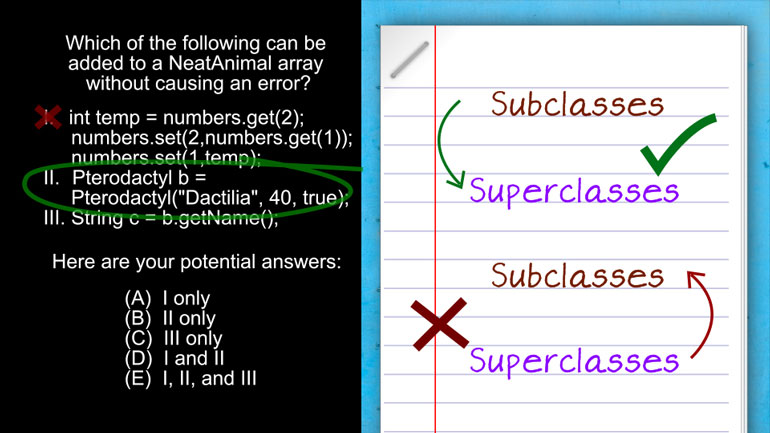
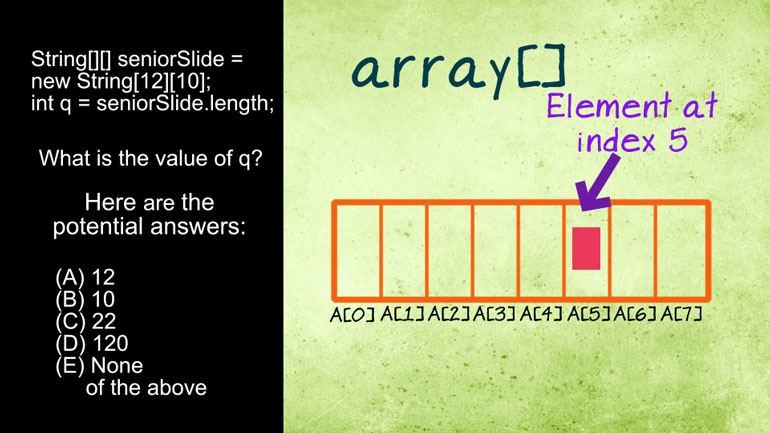
AP Computer Science 2.3 Classes and Objects. Which of the following is correct implementation of the Country class?
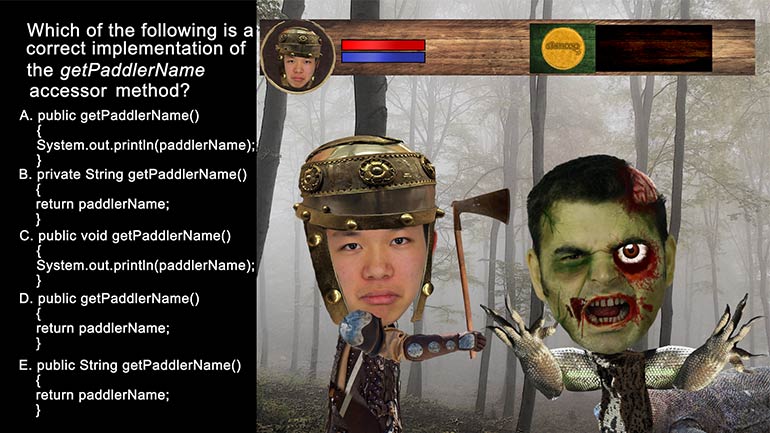
AP Computer Science 2.3 Program Development. What is correct implementation of the Emperor constructor method?
AP Computer Science 2.2 Review of the Basics 184 Views
Share It!
Description:
AP Computer Science 2.2 Review of the Basics. What is 23 (base 10) in base 2?
Transcript
- 00:00
Sorry Man here's your shmoop du jour Brought to you
- 00:05
by binary you'll find it a bit useful uncle All
- 00:12
right what is twenty three Base Ten in based who
- 00:16
And hear your potential answers So looks like we're being
- 00:24
asked to convert the base ten number twenty three into
Full Transcript
- 00:27
base to also known as binary while all major modern
- 00:31
civilizations used base ten numeral system and for good reason
- 00:35
Over tens of thousands of years we've come to realise
- 00:37
that ten fingers are really easy to countless when dealing
- 00:41
with a number higher than ten you just roll over
- 00:43
into a new set of ten it's about a simple
- 00:45
is it gets for us computers though think in terms
- 00:49
of off and on zero and one well that's all
- 00:52
well and good for counting up to zero in one
- 00:54
but we're two larger numbers come from and how are
- 00:57
they stored in a computer's memory Will the answer their
- 01:00
lives in using lots of zeros and ones zero or
- 01:04
one in memory is of idiot and with just eight
- 01:07
bits that are known as one bite you can count
- 01:11
all the way from zero to two hundred fifty five
- 01:14
each bit represents a different amount so starting from the
- 01:18
right side the first bit represents one If that first
- 01:22
bid is on or one we have a total value
- 01:25
in our bite of one The next bit over represents
- 01:29
two but here's where it begins to get oh so
- 01:31
clever bit after that represents four and the one after
- 01:35
that ate and after that sixteen and so on using
- 01:38
the power says too by flipping each differently valued bid
- 01:42
on or off we can count all the way up
- 01:44
to two hundred fifty five just add up which bits
- 01:47
are on and there's your number so this for example
- 01:50
is one hundred sixty seven right here and here's a
- 01:55
forty eight and here is two hundred anyway let's count
- 02:02
twenty three way already know that the fifth bit represent
- 02:05
sixteen so we'll turn that one on remember binary goes
- 02:09
from right to left How about the fourth bit representing
- 02:13
eight right here Eight plus sixteen would leave twenty for
- 02:16
which is over our target of twenty three so we'll
- 02:19
leave the fourth bidden as zero The third bit four
- 02:24
plus sixteen is twenty so yea progress second bit is
- 02:28
to turn our twenty two and the first bit is
- 02:32
one so turned that toe one and now when we
- 02:35
add it all up where twenty three or zero zero
- 02:38
zero one zero one one one in base too trailing
- 02:42
zeros can be left off and we're left with one
- 02:45
zero one one one that's Answer eh Well that was 00:02:51.25 --> [endTime] easy actually Quite difficult No
Related Videos
AP Computer Science 1.2 GridWorld Case Study and APIs. What is the direction of the actor?
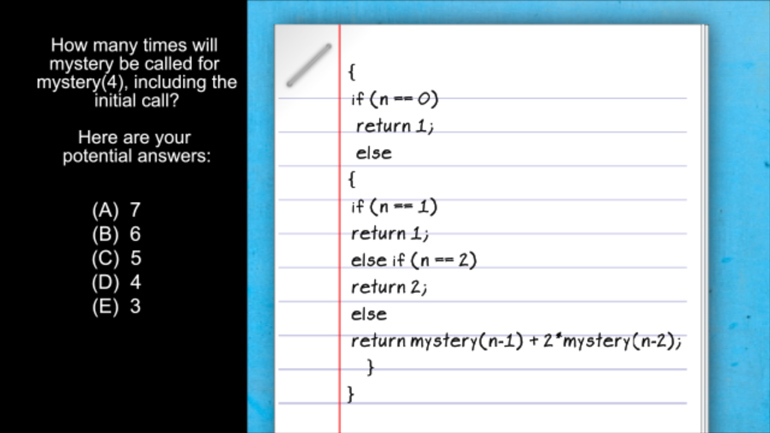
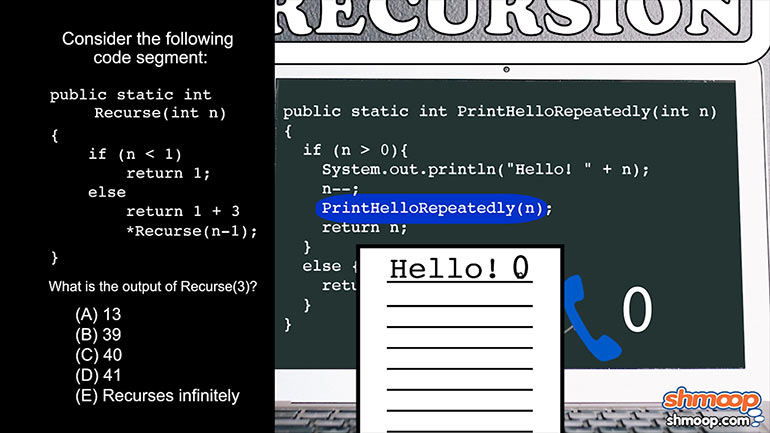
AP Computer Science 1.4 Standard Algorithms. How many times will mystery be called for mystery(n) for n > 1?
AP Computer Science 2.3 Classes and Objects. Which of the following is correct implementation of the Country class?
AP Computer Science 3.4 Inheritance, Abstraction, and Polymorphism. Which of the following will satisfy the conditional if statement for boo, str,...
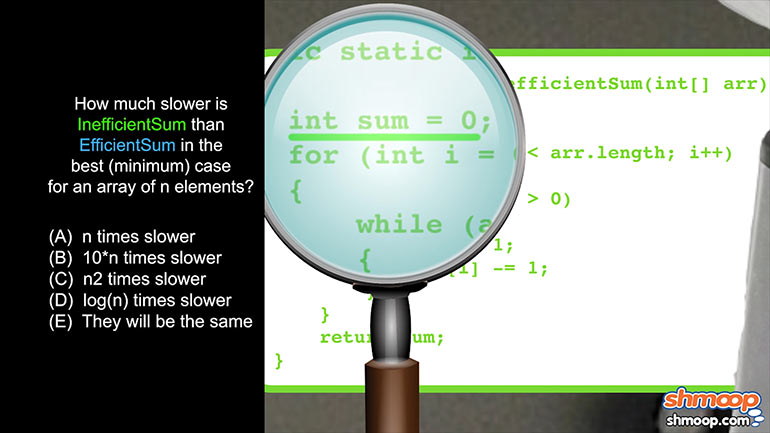
AP Computer Science 4.2 Standard Algorithms. What kind of algorithm is the following?