ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
AP Psychology Videos 135 videos
AP Psychology 2.3 Testing and Individual Differences. Which factor below needs to be considered in the administration and evaluation of the attenti...
AP Psychology 2.4 Testing and Individual Differences. Which of these is an example of studies used in the nature vs. nurture debate of intelligence?
AP Psychology 1.2 Developmental Psychology. How would you respond to someone stating that babies are born without any real sense of the world aroun...
AP Psychology 2.5 Motivation and Emotion 27 Views
Share It!
Description:
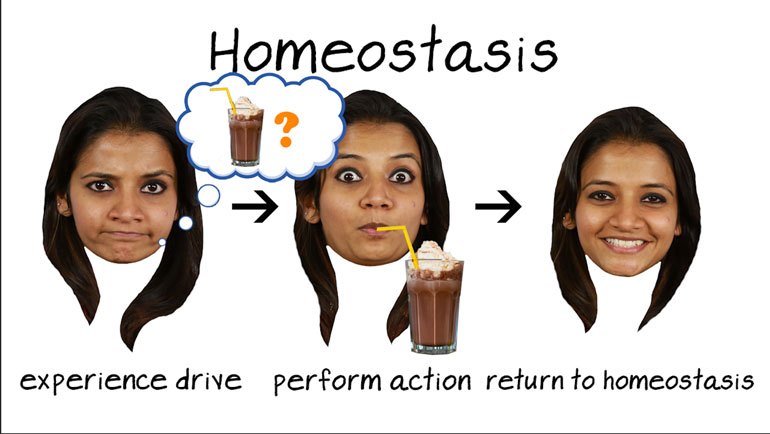
AP Psychology 2.5 Motivation and Emotion. Energy homeostasis is mostly controlled by the what?
Transcript
- 00:00
We speak student! And here's your shmoop du jour, brought to you by, the brain. Which
- 00:07
is far too fatty, for some zombies, gluten-free brain. Alright energy homeostasis
- 00:12
is the ideal rate of energy consumption that helps maintain body weight and is
- 00:16
mostly controlled by the, what? And here are the potential answers.
- 00:21
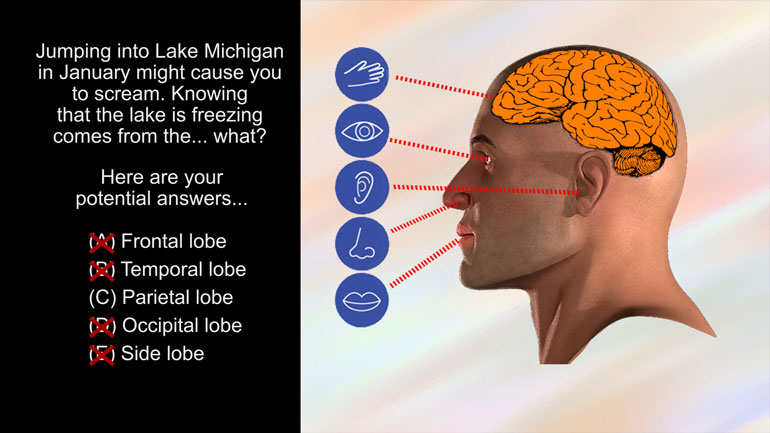
[murdering] Alright some of these are pretty funny. The brain is the
Full Transcript
- 00:27
main organ of the nervous system and it's found in all vertebrate and most [multiple choice and brain photo]
- 00:31
invertebrate animals and congressmen. Humans differ from most mammals, because
- 00:35
we have a much more developed cerebral cortex. This allows for better planning,
- 00:40
reasoning and abstract thought. Basically the reason we have zoos. So is
- 00:44
homeostasis controlled by B, the thalamus? Well the thalamus is involved in sensory
- 00:49
and motor signal relay, as well as the regulation of consciousness and sleep.
- 00:52
This is pretty important stuff, but it isn't what we're looking for in the [romans in coliseum]
- 00:55
question. Let's cross off B from our potential answers there. How about C,
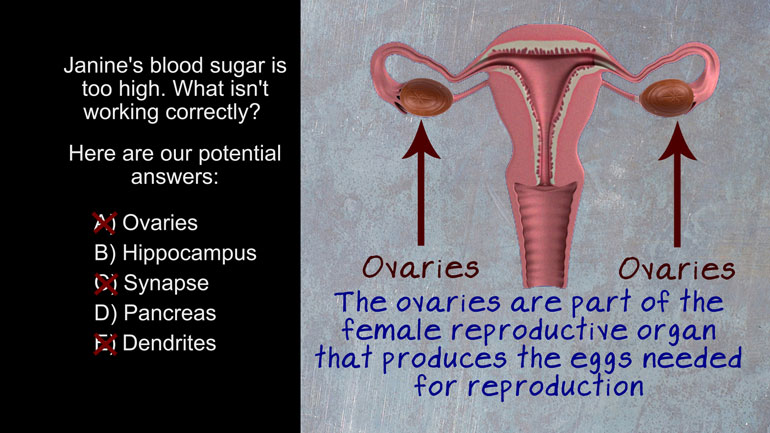
- 00:59
the amygdala. The amygdala is an almond-shaped mass of cells, that is
- 01:02
involved in many of our emotions and motivations. It also determines what
- 01:06
memories are stored in your brain. So again pretty cool, but not what we are after. So
- 01:10
cross off C. But would it be D, the hippopotamus, a hippocampus, sorry.
- 01:14
The hippocampus, which is not a university for a certain African animal, actually
- 01:19
plays a major role in long-term memory and spatial navigation. Not regulating [two hippopotamuses]
- 01:23
homeostasis, so ditch D. Perhaps it E, the fornix. Well the fornix, despite
- 01:28
sounding like an underground punk rock band, is actually a bundle of nerves that
- 01:31
carry signals from the hippocampus to other parts of the brain. If we cross E
- 01:35
off our list then we're just left with yeah A, the hypothalamus. The hypothalamus
- 01:40
controls homeostasis in part, by controlling the metabolic rate. Basically
- 01:44
it tells you when to eat, when to stop eating and other stuff. Oddly enough our
- 01:48
hypothalamus seems to shut down whenever we eat sour patch kids. Like well
- 01:53
that might be just us. So the correct answer is A, hypothalamus. Well we've
- 01:57
learned about quite a few parts of the brain, in this lesson. Maybe next week [picture of a brain]
- 02:01
we'll discover the part, that keeps getting Katy Perry songs stuck
- 02:04
our head. Baby you're a firework. We didn't say we could sing. Gluten-free brains.
Related Videos
AP Psychology 1.1 Social Psychology. Which of the following best describes social psychology?
AP Psychology 1.1 States of Consciousness. Who conducted research on REM sleep deprivations?
AP Psychology 1.2 Cognition. Which of the following strategies would work best for generating new ideas?
AP Psychology 1.2 Sensation and Perception. The cells in the back of the eye that only see in black and white are called what?
AP Psychology 1.2 Social Psychology. What is the best choice for producing better productivity?