ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
AP Physics 1 Videos 69 videos
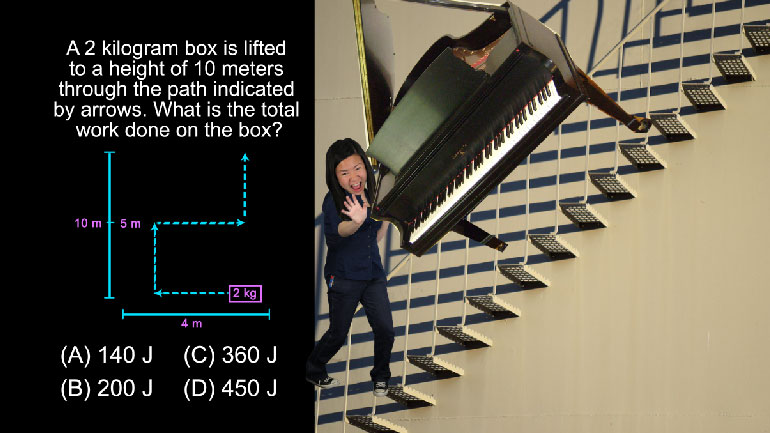
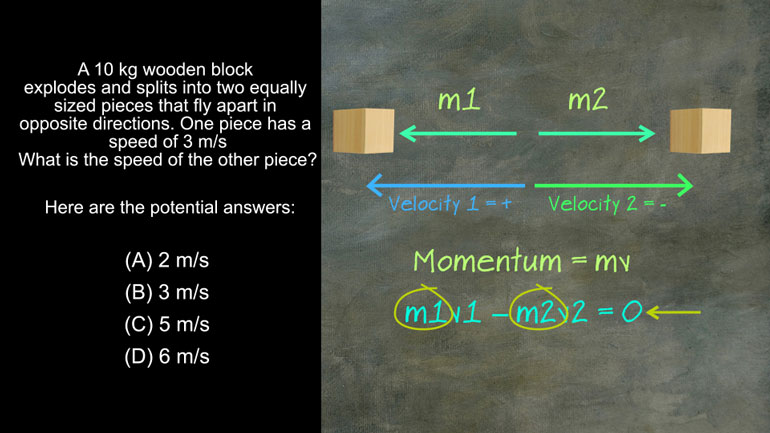
AP Physics 1: 3.3 Changes and Conservation Laws. What is the difference in work done?
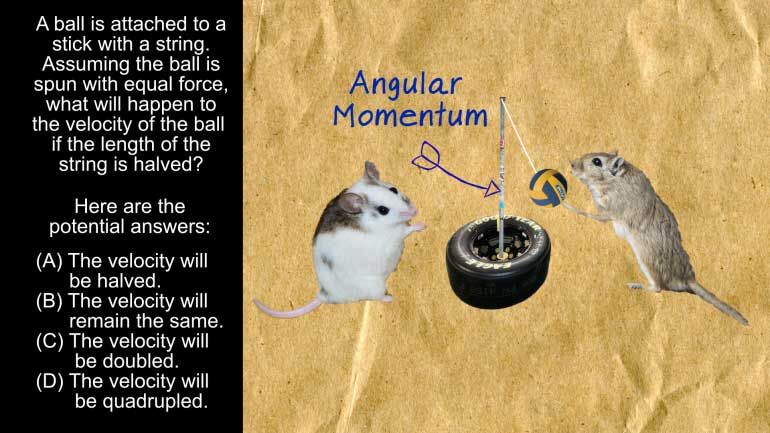
AP Physics 1: 3.5 Changes and Conservation Laws. Which of the following would increase the rate at which the plate spins?
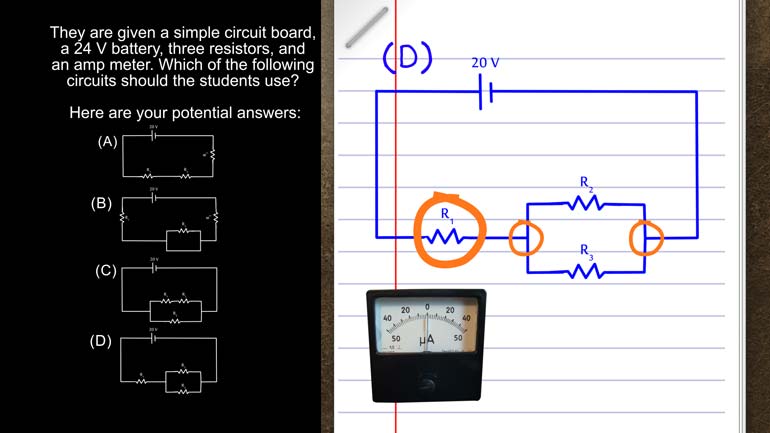
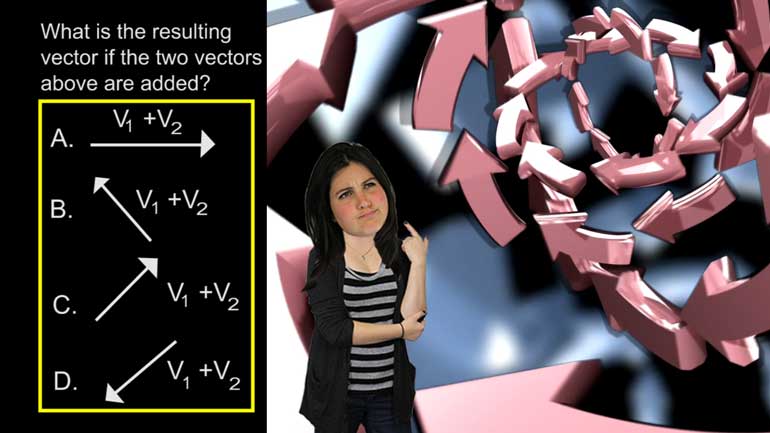
AP Physics 1: 2.4 Changes and Conservation Laws. Which of the following circuits should the students use?
AP Physics 1: 2.2 Fields in Space 316 Views
Share It!
Description:
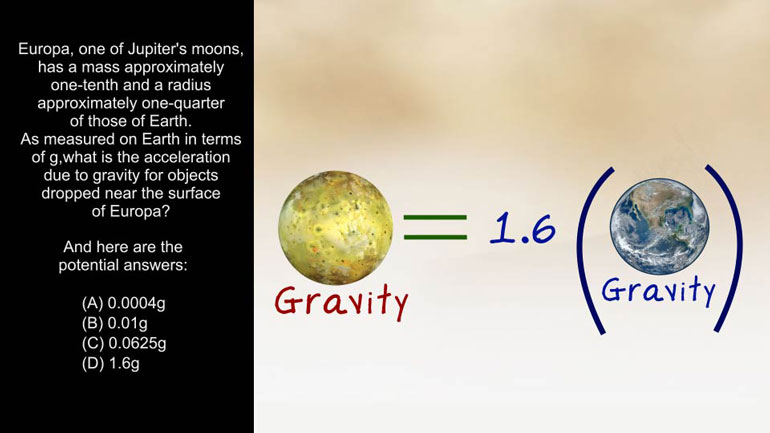
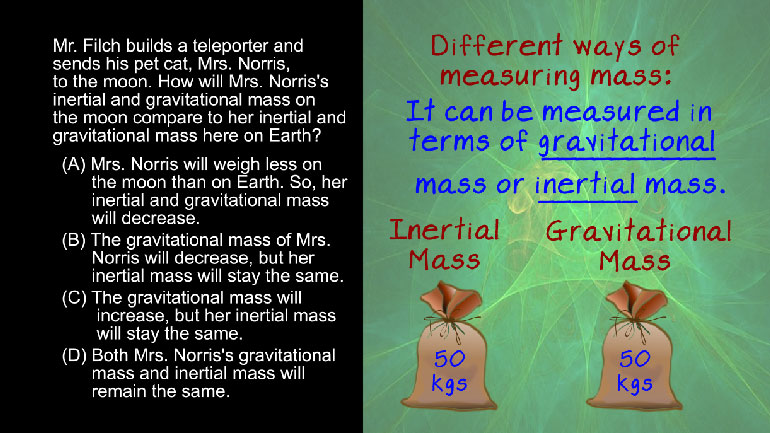
AP Physics 1: 2.2 Fields in Space. What is the acceleration due to gravity for objects dropped near the surface of Europa?
Transcript
- 00:00
Thank you We sneak and here's your shmoop du jour
- 00:05
brought to you by europa which is not a european
- 00:08
space colony Yet Europa one of jupiter's moons has a
- 00:13
mass approximately one tenth in a radius approximately one quarter
- 00:19
of those on earth as measured on earth In terms
Full Transcript
- 00:22
of g what is the acceleration due to gravity For
- 00:26
objects drop near the surface of europa And here the
- 00:29
potential answers Of course first thing we do once landing
- 00:36
on europa would be the trip Coming off our spaceship
- 00:39
would be one small step for man and one big
- 00:41
boobs for mankind welcoming shmoop All right so let's figure
- 00:45
out how hard that paul would be Luckily we know
- 00:47
how to calculate the surface gravity of an object The
- 00:50
formula is the gravitational constant or g multiplied by mass
- 00:54
divided by the square of the radius Well unfortunately we
- 00:58
don't have the numbers to plug into the formula because
- 01:01
we don't know the mass of a radius of europa
- 01:04
But what we do know is how europa's mass and
- 01:06
radius relate to first mass and radius So let's Think
- 01:10
about it like this The gravity of earth equals the
- 01:12
gravitational constant times the mass of the earth divided by
- 01:17
the square of the radius of the earth So to
- 01:20
see how europa's gravity relates to the earth's gravity are
- 01:23
equation would look about like this The gravity of your
- 01:26
over equals the gravitational constant times one tenth of the
- 01:30
earth's mass divided by the square of one quarter of
- 01:34
the earth's radius And now it can solve for the
- 01:37
ratio of point one point two Five squared which describes
- 01:41
the relationship between the mass and radius of europa Well
- 01:45
all we have to do is take point one and
- 01:46
divided by point both six to five and we get
- 01:49
one point Six That means the gravity of europa is
- 01:53
one point six times the gravity on earth making d
- 01:56
the correct answer All right well europe is pretty cool
- 01:59
name for a moon but maybe they'll name the next 00:02:01.726 --> [endTime] one something even cooler like alderaan or steve
Related Videos
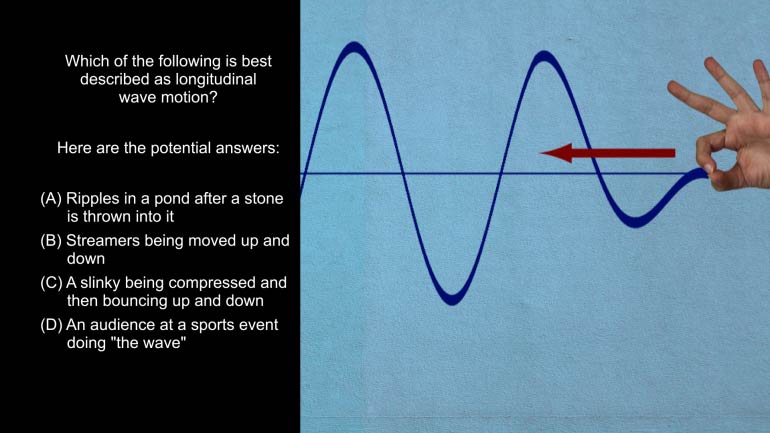
AP Physics 1: 1.4 Waves. Which of the following is technically true for Max as he stands at the edge of oblivion?
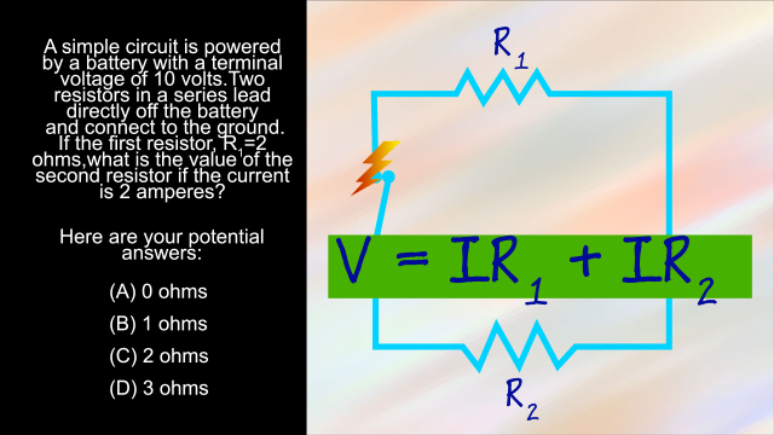
AP Physics 1: 1.4 Changes and Conservation Laws. Find the current across R2.
AP Physics 1: 2.4 Changes and Conservation Laws. Which of the following circuits should the students use?
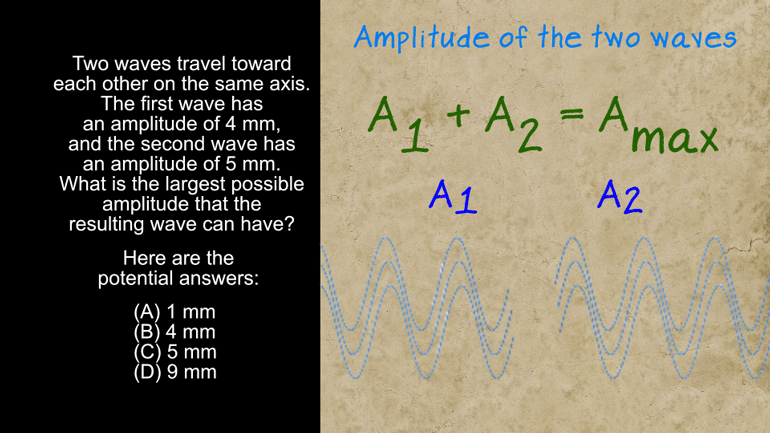
AP Physics 1: 1.5 Waves. What can possibly occur when the two waves reach each other?
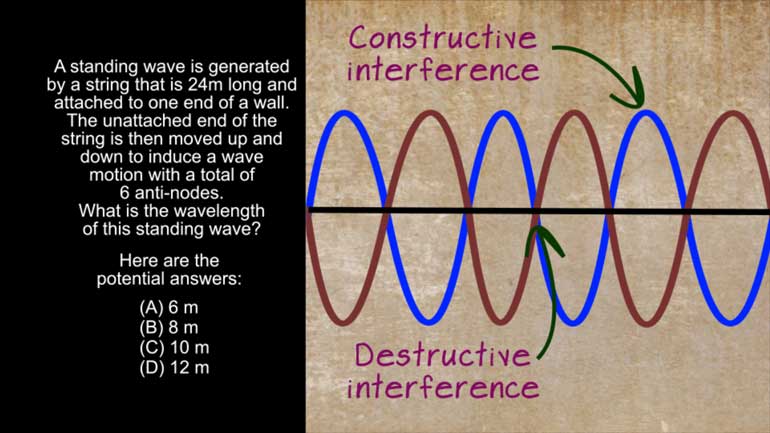
AP Physics 1: 2.2 Waves. What's the wavelength of this standing wave?